

Up: Period-Luminosity-Colour distribution and classification LPVs
This work is based on the LM method, which has been designed to fully exploit
the HIPPARCOS data to obtain luminosity calibrations. The mathematical
foundation of this method was presented in
Luri ([1995]) and Luri et al. ([1996a]).
Its main characteristics are:
- It is based on a maximum-likelihood algorithm;
- It is able to use all the available information on the stars: apparent
magnitude, galactic coordinates, trigonometric parallax, proper motions,
radial velocity and other relevant parameters (photometry, metallicity,
period, etc.), and takes into account, as an additional constraint, the
existence of mean relations between, e.g., period, luminosity and colour,
whose analytical form is given a priori;
- It allows a detailed modelling of the kinematics, the spatial
distribution, and also the distribution of luminosity, period and colour
of the sample.
In the implementation presented in this paper, the stars are assumed to be
exponentially distributed about the galactic plane and their velocities to
follow a Schwarzschild ellipsoid. The period and colour are assumed to
follow a bivariate normal distribution, including a correlation between the
two variables. This generates elliptic iso-probability contours in the
period-colour plane. For each given combination of period and colour, the
individual absolute magnitudes of the stars are assumed to be
normal-distributed about the mean value given by a
period-luminosity-colour relation, e.g.
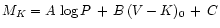 .
The resulting 3D distribution looks like a flattened ellipsoid whose main
symmetry plane is the PLC relation. All parameters of the model are
determined by maximum-likelihood estimation;
.
The resulting 3D distribution looks like a flattened ellipsoid whose main
symmetry plane is the PLC relation. All parameters of the model are
determined by maximum-likelihood estimation;
- The method takes into account the observational selection criteria that
were used when making the sample -- this is very important for obtaining
unbiased results (Brown et al. [1997]);
- It takes into account the effects of the observational errors; the
results are not biased by them and even low-accuracy data (which would
otherwise be useless) can be included;
- The galactic rotation is taken into account by introducing in the model
an Oort-Lindblad first-order differential rotation with A0=14.4,
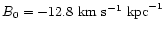 and
and
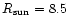 kpc;
kpc;
- The interstellar absorption is taken into account, using the 3D model
of Arenou et al. ([1992]).
A further important feature of the LM method is its capability to
separate and characterize, in the sample, groups of stars with
different properties (e.g. luminosity, kinematics, spatial distribution...).
The number of groups has to be fixed beforehand (see Sect. 4 for criteria).
Then, separate results are obtained for each group, and this provides a much
more meaningful information than a global result for the mixture of all of
them would.
For the population corresponding to each identified group, the LM method
provides unbiased estimates of the model parameters, i.e. for the version
used in this study:
- The parameters of the absolute magnitude distribution, i.e. the
coefficients of the mean period-luminosity-colour relation, and the
dispersion around it (
 );
);
- The velocity distribution: mean velocities
(U0,V0,W0)
and dispersions
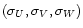 ;
;
- The spatial distribution: the scale heigth Z0;
- The period-colour index distribution: mean of the logarithm of the
period
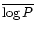 ,
mean de-reddened colour index, e.g.
,
mean de-reddened colour index, e.g.
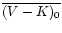 ,
the associated dispersions
,
the associated dispersions
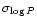 and,
e.g.,
and,
e.g.,
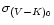 ,
and the correlation between log period and
colour;
,
and the correlation between log period and
colour;
- The percentage of the sample in each group: %.
In addition, the parameters of the selection function generating the sample
are obtained for each group.
The LM method also yields improved individual distance estimates (and thus
improved absolute magnitude estimates) which take into account all the
available information on each star: the trigonometric parallax
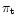 and other measurements (magnitude,
and other measurements (magnitude, 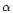 ,
,
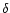 ,
,
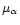 ,
,
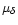 ,
,
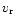 ,
P, colour). This estimation is free of
any bias due to observational selection or observational errors,
because both are taken into account by the method.
,
P, colour). This estimation is free of
any bias due to observational selection or observational errors,
because both are taken into account by the method.


Up: Period-Luminosity-Colour distribution and classification LPVs
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)
![]() .
The resulting 3D distribution looks like a flattened ellipsoid whose main
symmetry plane is the PLC relation. All parameters of the model are
determined by maximum-likelihood estimation;
.
The resulting 3D distribution looks like a flattened ellipsoid whose main
symmetry plane is the PLC relation. All parameters of the model are
determined by maximum-likelihood estimation;