![\begin{figure}
\includegraphics [width=4cm]{R42MATTESON_f1.eps}
\includegraphics [width=4.5cm]{R42MATTESON_f2.eps}
\vspace*{-3mm}\end{figure}](/articles/aas/full/1999/15/r42/Timg4.gif) |
Figure 1:
Prototype detector (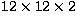 mm3). Left: Anode side; steering electrodes can be seen between
anode strips. Right: Detector installed in platform used in
laboratory and balloon flight tests. Strip detector left of center (cathode side on top) and
planar detector at far right mm3). Left: Anode side; steering electrodes can be seen between
anode strips. Right: Detector installed in platform used in
laboratory and balloon flight tests. Strip detector left of center (cathode side on top) and
planar detector at far right |