

Up: Iron line afterglows: General
At this meeting it has been reported the possible detection of an iron line
in the X-ray afterglow spectra of two bursts:
GRB 970508 detected by BeppoSAX
(Piro et al. 1999,
see also these
proceedings) and GRB 970828 by ASCA (Yoshida et al. these proceedings).
The significance of these features is admittedly not extremely
compelling (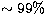 and
and  for the two events, respectively),
but the implications that they bear are so important
to justify a study on the radiation mechanisms that would produce it
(Lazzati et al. 1999,
see also these proceedings).
We can also put strong constraints on the size and mass
of the line emitting region in a model-independent way.
These limits, which are very robust, point towards the
presence, within a distance of
for the two events, respectively),
but the implications that they bear are so important
to justify a study on the radiation mechanisms that would produce it
(Lazzati et al. 1999,
see also these proceedings).
We can also put strong constraints on the size and mass
of the line emitting region in a model-independent way.
These limits, which are very robust, point towards the
presence, within a distance of 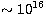 cm from the
burst, of at least 10-3
cm from the
burst, of at least 10-3 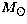 of iron.
We also stress that these emission line features, observed
in bursts which also have an optical afterglow, strongly suggest
that the line emitting region is not spherically symmetric,
but must have some degree of anisotropy.
Finally, this constrains the possible anisotropy of the burst
radiation, since the line emitting region samples different line
of sights than our own.
of iron.
We also stress that these emission line features, observed
in bursts which also have an optical afterglow, strongly suggest
that the line emitting region is not spherically symmetric,
but must have some degree of anisotropy.
Finally, this constrains the possible anisotropy of the burst
radiation, since the line emitting region samples different line
of sights than our own.
The cosmological parameters will be set throughout this paper to
H0 = 65 km s-1 Mpc-1, q0=0.5 and 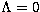 .
.


Up: Iron line afterglows: General
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)
![]() .
.