Following the data reduction steps described in Sect. 4, we have
obtained 31 emission-line images, one for each HCG of our sample.
We have computed both isophotal and adaptive-aperture H![]() fluxes for the HCG galaxies in the 31 fields by using SExtractor
(Bertin et al. 1996).
The full analysis of each image is divided in six steps:
sky background estimation, thresholding, deblending, filtering of the detections,
photometry and star/galaxy separation. For each continuum-subtracted H
fluxes for the HCG galaxies in the 31 fields by using SExtractor
(Bertin et al. 1996).
The full analysis of each image is divided in six steps:
sky background estimation, thresholding, deblending, filtering of the detections,
photometry and star/galaxy separation. For each continuum-subtracted H![]() image
we have used a detection threshold of one sigma above the background.
The H
image
we have used a detection threshold of one sigma above the background.
The H![]() isophotal fluxes have been computed within the region
defined by the detection threshold.
In addition to the isophotal flux we have also considered the corrected
isophotal flux estimated by SExtractor that should take into account the fraction of
flux lost by the isophotal one
(Bertin et al. 1996).
In addition the
adaptive-aperture photometry has also been calculated
(Kron 1980;
Bertin et al. 1996).
isophotal fluxes have been computed within the region
defined by the detection threshold.
In addition to the isophotal flux we have also considered the corrected
isophotal flux estimated by SExtractor that should take into account the fraction of
flux lost by the isophotal one
(Bertin et al. 1996).
In addition the
adaptive-aperture photometry has also been calculated
(Kron 1980;
Bertin et al. 1996).
Out of the 127 accordant observed galaxies belonging to the 31 HCG of our sample, we
have been able to compute isophotal and adaptive-aperture photometry
for 73 and 69 galaxies respectively.
The ![]() limiting flux, integrated within the mean seeing disk (2.3 arcsec),
reached in our observations ranges between
limiting flux, integrated within the mean seeing disk (2.3 arcsec),
reached in our observations ranges between ![]() and
and ![]() erg cm-2 s-1.
erg cm-2 s-1.
For 22 galaxies, which have not been detected in our H![]() images, we
have computed the 3
images, we
have computed the 3![]() upper limits above the background:
upper limits above the background:
![\begin{displaymath}
f_{\rm ul}= 3 \cdot {\rm rms} \cdot \left[\left(\frac{FWHM}{2} \right)^2 \cdot \pi
\right]^{\frac{1}{2}}\end{displaymath}](/articles/aas/full/1999/12/ds8462/img42.gif) |
(3) |
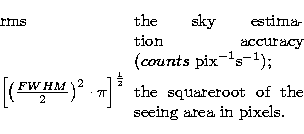
For the remaining 32 galaxies we have not been able to estimate the H![]() fluxes
because of one of the following reasons:
fluxes
because of one of the following reasons:
In Table 6 we list the galaxies for which it was not possible to measure their flux and the corresponding reason (1, 2, 3).
| |
(4) |

| (5) |
| (6) |
![\begin{displaymath}
Z_{\rm flux}=\frac{Z_{\rm flux_{\rm on}}}
{10^{[-0.4(k_{\rm ...
...cdot X_{\rm s})]}} \cdot
10^{[0.4(k_{\rm on} \cdot X_{\rm g})]}\end{displaymath}](/articles/aas/full/1999/12/ds8462/img56.gif) |
(7) |
 |
The H![]() fluxes have been then corrected for the galactic
extinction due to the gas and the dust of our Galaxy.
For each target galaxy we have computed the relative galactic hydrogen
column density
fluxes have been then corrected for the galactic
extinction due to the gas and the dust of our Galaxy.
For each target galaxy we have computed the relative galactic hydrogen
column density ![]() (atoms cm-2) as a function of the galaxy
coordinates (R.A. and Dec.).
(atoms cm-2) as a function of the galaxy
coordinates (R.A. and Dec.).
![]() was obtained interpolating the data available from the
Stark et al. (1992)
data-base.
We computed also an interpolation error defined as the mean of
differences weighted on the distances.
Using the relations:
was obtained interpolating the data available from the
Stark et al. (1992)
data-base.
We computed also an interpolation error defined as the mean of
differences weighted on the distances.
Using the relations:
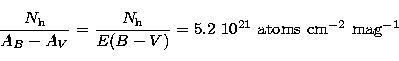 |
(8) |
 |
(9) |
| (10) |
The H![]() fluxes of spirals have also been corrected for the
Internal Extinction due to the interstellar medium inside the target galaxy
itself.
This correction in the blue band is usually obtained by summing to the galaxy
magnitude the value
fluxes of spirals have also been corrected for the
Internal Extinction due to the interstellar medium inside the target galaxy
itself.
This correction in the blue band is usually obtained by summing to the galaxy
magnitude the value
| (11) |

| (12) |
On the basis of the fluxes thus obtained we have derived the H![]() luminosity L
luminosity L![]() of galaxies:
of galaxies:
| (13) |
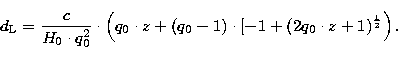 |
(14) |
In Table 7 we report the isophotal luminosities of the galaxies (![]() )uncorrected for Galactic and Internal Extinction.
)uncorrected for Galactic and Internal Extinction.
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)