Given its generality, the algorithm is portable to other detectors. In
the case of the ROSAT HRI, we have used the same cell geometry,
but different choices of ![]() and
and ![]() . We adopted the PSF given
by David et al. (1995) and we have verified that the highest
value of
. We adopted the PSF given
by David et al. (1995) and we have verified that the highest
value of ![]() usable for count extraction purposes is 0.85. For greater
usable for count extraction purposes is 0.85. For greater
![]() , the calculation of the cell radius involves integration of
the tails of the PSF rather than the core, and since the tail is less
well known than the core, that would yield high uncertainties in the
assessment of the cell's size.
, the calculation of the cell radius involves integration of
the tails of the PSF rather than the core, and since the tail is less
well known than the core, that would yield high uncertainties in the
assessment of the cell's size.
We have performed simulations similar to those described in the PSPC
case. We verified that the screening algorithm is more efficient when
tailored on a template source lying at 15![]() off-axis in the HRI
FOV. Since the HRI FOV is
off-axis in the HRI
FOV. Since the HRI FOV is ![]() ,
this result is therefore similar to the PSPC case, in which the
optimal template source lies at 30
,
this result is therefore similar to the PSPC case, in which the
optimal template source lies at 30![]() off-axis in a
off-axis in a ![]() radius FOV.
radius FOV.
We have also verified that the screening procedure yields very low gain
on detected sources (![]() %). The corresponding rejection
percentages are also negligible, usually between 1 and 3% of the total
exposure times. We stress that this result is not due to low background
counting statistics in the detection cell, because the ratio between the
number of source and background counts in the cell is
%). The corresponding rejection
percentages are also negligible, usually between 1 and 3% of the total
exposure times. We stress that this result is not due to low background
counting statistics in the detection cell, because the ratio between the
number of source and background counts in the cell is ![]() in both
PSPC and HRI typical observations. Other explanations of the low HRI
screening efficiency could be:
in both
PSPC and HRI typical observations. Other explanations of the low HRI
screening efficiency could be:
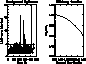
Figure 3: Same as Fig. 2 (click here) but for the background light
curve of an HRI field pointed towards the
NGC 2422 open cluster (38075 s)
Figure 3 (click here), left panel, reports the light curve of an HRI
case study, a sequence pointed toward the NGC 2422 open cluster with
![]() detected sources (RH 201828, Barbera et al. in preparation).
detected sources (RH 201828, Barbera et al. in preparation).
After inspecting a number of HRI real background light-curves, we conclude that the screening of HRI data is not a crucial point in HRI data analysis, but it could likely be very effective when the particle and/or the SB spikes heavily contaminates the data. This may occur either when the spike amplitudes are large (like in PSPC) or when the mean background level is low (this may be the case of the AXAF detectors).