|
 | normalized antenna power pattern |
|
| Eq. (1 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
r | angular distance between the center |
|
| of the antenna beam and the target position |
|
| Eq. (3 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 | ratio of measured boresight antenna |
|
| temperature to expected source antenna |
|
| temperature |
|
| Eq. (14 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 | normalized signal difference between two |
|
| successive positions of the antenna beam on the |
|
| circular path |
|
| Eq. (17 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 | measured antenna temperature |
|
| of the pointing source |
|
| Eq. (4 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
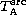 | expected antenna temperature of the pointing |
|
| source at center of the antenna beam |
|
| Eq. (5 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 , , 
| measured power ON-source and OFF-source, |
|
 | respectively;  |
|
| Eq. (1 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 | cartesian coordinates of the beam center |
|
| (cross-elevation and elevation) |
|
| Eq. (2 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
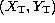 | cartesian coordinates of the target |
|
| (cross-elevation and elevation) |
|
| Eq. (8 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 | radius of the circular path |
|
| described by the antenna beam center |
|
| Eq. (2 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
 | angular distance between the |
|
| optical axis and the target |
|
| Eq. (8 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
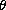 | angle defining the position of the center of |
|
| the antenna beam with respect to the X axis |
|
| Eq. (2 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
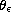 | angle defining the unknown position of the |
|
| target with respect to the X axis |
|
| Eq. (8 (click here)) |
|
| |
|
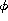 | instrumental phase offset used in |
|
| the dot-product method |
|
| Eq. (18 (click here)) |
|
| |