where t is the observation time (ET),
where
where f is the focal length of the camera and Pi is the
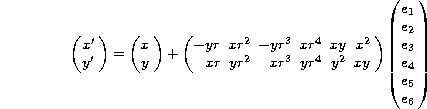
where r2=x2+y2 and the ei are the distortion coefficients. Lastly convert from the focal plane coordinates into pixel and line:
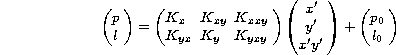
where
The Voyager observations of Phoebe appear in Table 10 (click here) in the form of the pixel and line locations in the Voyager camera frame. The table also gives the inertial camera pointing angles which were derived from the background star images. As a simplification, the effects of uncertainty in the pointing have been incorporated into the location accuracies quoted in the table. The observations have not been corrected for stellar aberration; they provide measures of the apparent position of Phoebe as seen from the spacecraft.
| Picture ID | Observation time (UTC) | Camera pointing angles (deg) | Pixel | Line | ||||
| Rt. Ascen. | Dec. | Twist | Value | Acc. | Value | Acc. | ||
| 41901B+37 | 17 Jun. 1981 00:11:52.12 | 203.323974 | -7.744627 | -129.273157 | 465.80 | 0.71 | 589.34 | 0.61 |
| 42182B+27 | 26 Jun. 1981 08:51:52.12 | 205.345157 | -8.780149 | -127.860860 | 492.73 | 0.60 | 402.65 | 0.58 |
| 42351B+55 | 02 Jul. 1981 00:26:11.21 | 206.845295 | -9.510055 | -127.253253 | 571.33 | 0.67 | 319.07 | 0.65 |
| 42800B+50 | 16 Jul. 1981 23:34:11.21 | 212.089857 | -11.710938 | -123.628497 | 372.56 | 0.58 | 381.50 | 0.58 |
| 43300B+39 | 02 Aug. 1981 15:25:32.81 | 222.738376 | -15.963989 | -118.780588 | 422.66 | 0.70 | 140.20 | 0.58 |
| 43461B+08 | 07 Aug. 1981 23:48:44.81 | 228.634792 | -17.725684 | -115.402728 | 339.80 | 0.70 | 547.97 | 0.62 |
| 43491B+27 | 09 Aug. 1981 00:03:56.81 | 230.085968 | -18.288527 | -115.301906 | 642.37 | 0.57 | 388.94 | 0.58 |
| 43696B+50 | 15 Aug. 1981 20:22:19.85 | 241.941386 | -21.485373 | -110.265804 | 323.33 | 0.66 | 399.83 | 0.66 |
|
| ||||||||
To process the observations, first compute the apparent position of Phoebe:
![]()
where t is the observation time (ET), ![]() is the light travel time from
the Phoebe to the spacecraft,
is the light travel time from
the Phoebe to the spacecraft, ![]() is Phoebe's position vector,
is Phoebe's position vector, ![]() is the spacecraft position vector, and
is the spacecraft position vector, and ![]() is the Saturnian system
barycenter position vector; the former two positions are relative to the
Saturnian system barycenter, and the latter is relative to the Solar System
barycenter. The vectors
is the Saturnian system
barycenter position vector; the former two positions are relative to the
Saturnian system barycenter, and the latter is relative to the Solar System
barycenter. The vectors ![]() and
and ![]() are the respective
velocities of the spacecraft and Saturnian system barycenter. This computation
implicitly involves an iterative procedure to determine
are the respective
velocities of the spacecraft and Saturnian system barycenter. This computation
implicitly involves an iterative procedure to determine ![]() from the true
relative distance between Phoebe and the spacecraft.
Next rotate the apparent position into camera body coordinates:
from the true
relative distance between Phoebe and the spacecraft.
Next rotate the apparent position into camera body coordinates:
![]()
where ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are the right ascension, declination, and
twist camera pointing angles from Table 10 (click here), and
are the right ascension, declination, and
twist camera pointing angles from Table 10 (click here), and ![]() is
the standard
is
the standard
![]() rotation matrix about the
rotation matrix about the ![]() axis.
Then project the camera body coordinates into the focal plane via the gnomonic
projection:
axis.
Then project the camera body coordinates into the focal plane via the gnomonic
projection:
![]()
where f is the focal length of the camera and Pi is the ![]() component of the vector
component of the vector ![]() .
The focal plane coordinates must be corrected for electromagnetic and
optical distortion:
.
The focal plane coordinates must be corrected for electromagnetic and
optical distortion:
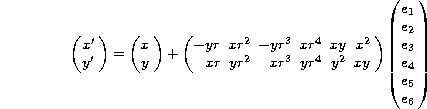
where r2=x2+y2 and the ei are the distortion coefficients.
Lastly convert from the focal plane coordinates into pixel and line:
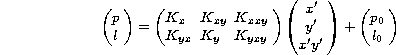
where ![]() is the camera transformation matrix and p0,l0 are
the pixel and line location of the optical axis.
is the camera transformation matrix and p0,l0 are
the pixel and line location of the optical axis.
For the Voyager 2 narrow angle camera the focal length is 1503.49 mm,
the optical axis is located at (398.07, 401.95),
the elements of the conversion matrix ![]() are:
are:
![]()
and the distortion coefficients are:
![]()
| Picture ID | Position (km) and Velocity (km/s) | ||
| x | y | z | |
| 41901B+37 | 63212533.0 | 19188537.5 | 4918608.4 |
| -10.271438 | -3.060466 | -0.771611 | |
| 42182B+27 | 54904032.8 | 16712535.5 | 4294300.1 |
| -10.274296 | -3.062307 | -0.772204 | |
| 42351B+55 | 49888808.0 | 15217592.1 | 3917311.5 |
| -10.277604 | -3.063816 | -0.772655 | |
| 42800B+50 | 36591667.8 | 11252598.7 | 2917747.4 |
| -10.295356 | -3.070303 | -0.774463 | |
| 43300B+39 | 21738982.8 | 6823497.4 | 1799317.7 |
| -10.350959 | -3.087303 | -0.779872 | |
| 43461B+08 | 16946391.4 | 5393865.6 | 1438146.6 |
| -10.390964 | -3.100103 | -0.783285 | |
| 43491B+27 | 16038694.3 | 5123047.7 | 1369718.5 |
| -10.401263 | -3.103412 | -0.784171 | |
| 43696B+50 | 9856547.4 | 3277698.5 | 903262.8 |
| -10.521137 | -3.142626 | -0.794836 | |
|
| |||
Table 11 (click here) contains the Voyager position, ![]() , and velocity,
, and velocity,
![]() , vector components at the observation times.
, vector components at the observation times.