

Up: The absorption spectrum
We have presented high-resolution spectra of
the quasar PKS 2126-158.
The analysis of the Ly forest
shows that:
forest
shows that:
- The peak value of the Doppler parameter distribution is
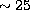 km
s-1.
This value is large enough to be in agreement
with a standard ionization model, but not too high
(
km
s-1.
This value is large enough to be in agreement
with a standard ionization model, but not too high
(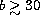 km s-1)
to make the Ly
km s-1)
to make the Ly clouds contribution to baryonic matter
exceed the standard nucleosynthesis value (Hu et al. 1995).
clouds contribution to baryonic matter
exceed the standard nucleosynthesis value (Hu et al. 1995).
- The plot of the statistical sample of Ly
 lines in the
lines in the 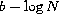 plane shows no significant correlation between the two parameters.
plane shows no significant correlation between the two parameters.
- The column density distribution shows a cutoff, due to
incompleteness and blending, for
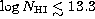 ,
for higher values it is well described by a power-law
,
for higher values it is well described by a power-law
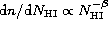 with
with 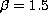 (Hu et al. 1995; Giallongo et al. 1996).
(Hu et al. 1995; Giallongo et al. 1996).
- The number density of lines per unit redshift
is in agreement with a standard power-law evolution of
the type
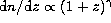 with
with 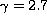 (Giallongo et al. 1996).
(Giallongo et al. 1996).
Clustering properties of the Ly lines have been investigated in another
paper (Cristiani et al. 1997). Ly
lines have been investigated in another
paper (Cristiani et al. 1997). Ly of higher column density
(
of higher column density
(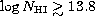 ) are found to cluster significantly
on scales around 100 km s-1.
) are found to cluster significantly
on scales around 100 km s-1.
From the analysis of metal absorptions the following results have been
obtained:
- Two new C IV absorption systems have been detected at z=3.2165
and z=2.5537.
- A mean metallicity of
 dex solar has been found
using the metal systems at z=2.8195, z=2.9072 and
z=2.9675.
In order to make the column densities of the intervening
systems compatible
with realistic assumptions about the cloud sizes and the [Si/C] ratios,
it is necessary to assume
an increase of a factor 10 in the jump at 4 Ryd of the standard spectrum
of the ionizing UV background (Haardt & Madau 1997).
dex solar has been found
using the metal systems at z=2.8195, z=2.9072 and
z=2.9675.
In order to make the column densities of the intervening
systems compatible
with realistic assumptions about the cloud sizes and the [Si/C] ratios,
it is necessary to assume
an increase of a factor 10 in the jump at 4 Ryd of the standard spectrum
of the ionizing UV background (Haardt & Madau 1997).
- Merging the present data with those obtained
at comparable resolution for the two
quasars Q0055-26 and Q0000-26, has provided a relative large sample
(71 doublets) of C IV absorptions, complete down to a
column density
 .
The C IV column density distribution is well fitted by a
single power-law, with
.
The C IV column density distribution is well fitted by a
single power-law, with  .
.
- The mode of the Doppler parameter distribution is
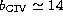 km -1.
km -1.
- The clustering properties of the individual components of the C IV
features have been investigated making use of a TPCF in the velocity space.
A significant signal is obtained for scales smaller than 200-300 km
s-1,
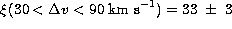 .
The result is consistent with previous findings
(Sargent et al. 1988; Heisler et al. 1989) when the
increased resolution and s/n ratio of the present data is taken into account.
.
The result is consistent with previous findings
(Sargent et al. 1988; Heisler et al. 1989) when the
increased resolution and s/n ratio of the present data is taken into account.
- Correlations between total equivalent widths and number of
components and between total equivalent widths and velocity spread of
the individual C IV systems are observed.
The two-point correlation functions for lower column density C IV
absorption systems, recently estimated by Womble et al. (1997) and
Songaila & Cowie (1996), show a weaker signal than the present data.
These three pieces of evidence suggest a trend of decreasing
clustering amplitude with decreasing column density.
An analogous behaviour has been observed
for Ly
 lines by Cristiani et al. (1997).
lines by Cristiani et al. (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Madau, C. Porciani and S. Savaglio for enlightening discussions.
SC acknowledges the support of the ASI contract 95-RS-38 and
of the TMR-network of the European Community "Galaxy Formation and
Evolution''.


Up: The absorption spectrum
Copyright by the European Southern Observatory (ESO)
web@ed-phys.fr
![]() forest
shows that:
forest
shows that:
![]() lines have been investigated in another
paper (Cristiani et al. 1997). Ly
lines have been investigated in another
paper (Cristiani et al. 1997). Ly![]() of higher column density
(
of higher column density
(![]() ) are found to cluster significantly
on scales around 100 km s-1.
) are found to cluster significantly
on scales around 100 km s-1.