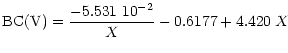 |
|||
The following stars departed more than
![]() in either of the final fits:
in either of the final fits:
BS4902 (2.8), BD-180271 (2.5), BS2286 (7.3), BS7523 (5.2),47Tuc-1421 (2.8), 47Tuc-3512 (3.4), 47Tuc-7320 (4.8), 47Tuc-1414 (2.5), 47Tuc-1518 (2.6), 47Tuc-4411 (3.1), 47Tuc-6509 (3.9), M71-B (2.9), HD 088609 (3.1), BS8930 (2.6),
HD 171496 (4.7), BS3547 (2.8). We show in Fig. 16 the mean lines
corresponding to (17) and (18), together with the residuals of the fit.
In the range
![]() relation (18) is not suited to
deriving accurate bolometric corrections since on the one hand the
dispersion of the fit is around 2.5% (0.025 mag) due to the fact that
cool temperatures have greater internal errors, and on the other, the variation
of BC(V) with log
relation (18) is not suited to
deriving accurate bolometric corrections since on the one hand the
dispersion of the fit is around 2.5% (0.025 mag) due to the fact that
cool temperatures have greater internal errors, and on the other, the variation
of BC(V) with log
![]() is very steep. A noticeable feature of the
present scale is the significant
variation of the bolometric correction with metallicity, especially in
the range of higher temperatures (this point is emphasized in Fig. 16). Although a systematic bias in the data can never be completely discarded, the size of the effect found is not compatible either with photometric
errors, or with the internal uncertainties in temperatures.
is very steep. A noticeable feature of the
present scale is the significant
variation of the bolometric correction with metallicity, especially in
the range of higher temperatures (this point is emphasized in Fig. 16). Although a systematic bias in the data can never be completely discarded, the size of the effect found is not compatible either with photometric
errors, or with the internal uncertainties in temperatures.
In Fig. 17, we show the comparison between the present calibration and
several theoretical and empirical calibrations previously published. Differences in the zero-point caused by the adopted bolometric correction of the sun have
been taken into account. In the range 8000 K
![]() 6000 K our
scale is systematically over the other scales considered (
6000 K our
scale is systematically over the other scales considered (![]() mag), in the range 6000 K
mag), in the range 6000 K
![]() 4000 K differences are symmetrically distributed in a band of
4000 K differences are symmetrically distributed in a band of ![]() mag. These
differences show the existence of essential problems in deriving bolometric corrections. In the
case of empirical calibrations the possible causes of discrepancies might be the absolute flux calibration, the way of fixing the
zero-point and an insufficient discrimination of the metallicity effect. In
the case of theoretical calibrations, the possible causes are drawbacks in the model atmospheres and/or
difficulties in the synthesis of colours.
mag. These
differences show the existence of essential problems in deriving bolometric corrections. In the
case of empirical calibrations the possible causes of discrepancies might be the absolute flux calibration, the way of fixing the
zero-point and an insufficient discrimination of the metallicity effect. In
the case of theoretical calibrations, the possible causes are drawbacks in the model atmospheres and/or
difficulties in the synthesis of colours.
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)