

Up: X-ray afterglow of gamma-ray
One year and a half ago BeppoSAX discovered the X-ray
afterglow source associated to GRB 980228
(Costa et al. 1997).
Following
this first discovery an impressive collection of new
data and a real outburst of interpretation work has rejuvenated all
this topic of Astrophysics. These mysterious objects are nowadays
less elusive but the amount of problems open probably
is not decreased. The expectation is now funded that
the Astrophysics Gamma-Ray Burst is taking the place of the
"Mystery of Gamma Ray Bursts". GRBs have become the crossroad of
a network of knowledge
including association with other phenomena, study of parent
objects and probe of ancient universe at a scale of distance
deeper than that of Supernovae.
This discovery was possible with a special use of all the
capabilities of BeppoSAX satellite. In the initial
configuration that made the first result possible
the sequence for the detection of GRB afterglows was:
- a) An onboard trigger from Gamma Ray Burst Monitor;
- b) A detection with Quick Look Analysis of a burst in
the X-ray rate meters coincident with a);
- c) Imaging of the burst by processing data of the WFC;
- d) Pointing of the GRB direction with Narrow Field Instruments.
Now the situation has evolved. BeppoSAX is still the main producer of
data on GRBs and their afterglow, but not only as an independent
instrument. It is now part of a network that is significantly
increasing the total amount of data and their significance. The
major improvements (and the associated results) with respect to
the original procedure are:
- a) Other triggers are used to search for the bursts in
the WFC. In particular 2 GRBs have been detected with a
trigger from BATSE experiment aboard CGRO;
- b) GRB positions are determined and distributed with
increasing precision and decreasing delay, by an independent
distribution system and by GCN. One of the
transient sources (GRB 980326) has been detected in the optical
band without any pointing with NFIs;
- c) Positions originated from other experiments (ASM-XTE,
PCA, IPN) have been included in the alert loop and one X-ray
transient has been found with BeppoSAX NFIs in a burst
direction determined by ASM (GRB 980703);
- d) GRB 980613 has been detected without any on-board
gamma-ray trigger but only from the Quick Look
inspection of X/Gamma-rays light curves.
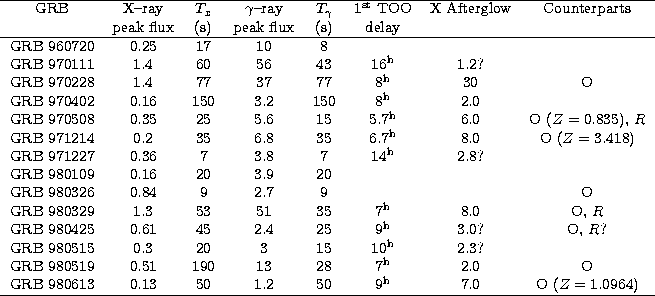
Table 1:
GRBs detected and localized with BeppoSAX GRBM and
WFCs.
The peak fluxes are in units
of 10-7 erg cm-2 s-1.
The Afterglow Sources are given in units
of 10-13 erg cm-2 s-1 around 8
hours after the GRB
 |


Up: X-ray afterglow of gamma-ray
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)

