

Up: Gamma-ray burst afterglow observations
The observation of a gamma-ray burst afterglow using AXAF can be used
for several purposes. The use of the time depends upon how long the
observation time is. For a very short observation  s,
obtaining the burst position shortly after the burst is the best use of
the time. If the optical counterpart has already been detected, then
AXAF can add little to the observation. If no optical counterpart is
detected within a day, then the accurate X-ray position will permit
association to be made with a galaxy to a very deep limiting magnitude,
28-30 mv. For the soft gamma-ray repeaters which are observable out
to
s,
obtaining the burst position shortly after the burst is the best use of
the time. If the optical counterpart has already been detected, then
AXAF can add little to the observation. If no optical counterpart is
detected within a day, then the accurate X-ray position will permit
association to be made with a galaxy to a very deep limiting magnitude,
28-30 mv. For the soft gamma-ray repeaters which are observable out
to  Mpc a significant flux of fluorescent photons might be
observable for a time of
Mpc a significant flux of fluorescent photons might be
observable for a time of 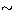 days.
days.
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was supported by NASA under contract No. NAS8-38252.
The author wishes to thank Audrey
Garmire for some useful calculations and comments, and Neil Gehrels and
Fiona Harrison for a useful discussion.


Up: Gamma-ray burst afterglow observations
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)