(1). Find the position of
the innermost point of a spiral
arm and measuring its coordinate (![]() ) relative to the image center and
to the major axis.
) relative to the image center and
to the major axis.
(2). Vary the value of the inclination ![]() around
around
![]() ) and fit the spiral arm
starting from that innermost point with
a logarithmic spiral curve to get its winding parameter
) and fit the spiral arm
starting from that innermost point with
a logarithmic spiral curve to get its winding parameter ![]() such that
such that ![]() , where m is the number of arms,
with a least square method.
D25 and d25 are taken from the Third Catalog
of Bright Galaxies by de Vaucouleurs et al. (1991, RC3).
They are the apparent major and minor isophotal diameters measured at or
reduced to the surface brightness level
, where m is the number of arms,
with a least square method.
D25 and d25 are taken from the Third Catalog
of Bright Galaxies by de Vaucouleurs et al. (1991, RC3).
They are the apparent major and minor isophotal diameters measured at or
reduced to the surface brightness level ![]() blue mag per square
arc second.
blue mag per square
arc second.
(3). Determine the inclination and the corresponding winding parameter by comparing the fitted spiral curve with the image.
(4). Calculate the thickness of the galactic disk h, by
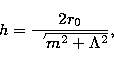 |
(1) |
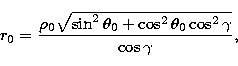 |
(2) |
(5). The thickness of the galactic disk, H in kpc, is
| H=hd, | (3) |
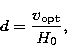 |
(4) |
Our statistical sample contains 71 galaxies,
selected from more than 600 northern spirals
having a determined ![]() (i.e., the total color index
corrected for galactic and internal extinction
and redshift)
in RC3 according to one single criterion: their images have
distinguishable spiral arms.
The mean Hubble type indexes (T) of these galaxies
are from 2 to 6, and
they have
(i.e., the total color index
corrected for galactic and internal extinction
and redshift)
in RC3 according to one single criterion: their images have
distinguishable spiral arms.
The mean Hubble type indexes (T) of these galaxies
are from 2 to 6, and
they have ![]() ) less than 0.76.
) less than 0.76.
Our data reduction and analyses
were done with IRAF![]() installed in the Sun Workstation
at the Laboratory of Astronomical Data Analysis of Nanjing University.
installed in the Sun Workstation
at the Laboratory of Astronomical Data Analysis of Nanjing University.
Copyright The European Southern Observatory (ESO)