

Up: GRANAT/WATCH catalogue of
From December 1989 to September 1994 the astrophysical observatory
GRANAT performed pointed observations of different celestial
regions. During that period, the
X-ray instrument WATCH, a part of the
scientific payload of the observatory, was monitoring the whole of the
sky. WATCH is uniquely capable of precisely measuring the celestial
positions (the radius of the localization region is generally smaller
than 1 deg at the 3 confidence level) of short-lived hard
X-ray sources, which include GRBs. Another feature of the instrument
relevant to observations of GRBs is that its detectors are sensitive over an
X-ray energy range that reaches down to
confidence level) of short-lived hard
X-ray sources, which include GRBs. Another feature of the instrument
relevant to observations of GRBs is that its detectors are sensitive over an
X-ray energy range that reaches down to 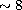 keV, the domain where the
properties of GRBs are known less than at higher energies.
keV, the domain where the
properties of GRBs are known less than at higher energies.
In this paper, we present the catalogue of GRBs detected with WATCH in
1989-1994. For nearly half of the events we
have been able to determine the location of the burst source on the
celestial sphere. Earlier, a preliminary catalogue covering the WATCH
observations carried out before October 1992 was compiled by
Castro-Tirado (1994). The new catalogue has been updated mainly
in the two aspects: 1) the bursts detected between October 1992 and September
1994 have been added, 2) more accurate positions have been
determined for many of the previously catalogued events due to the use
of more precise information on the spacecraft attitude and an improved
model of the instrument.
Copyright by the European Southern Observatory (ESO)