

Up: Correction of the
Interferometric measurements of fundamental parameters of stars are
common applications of astronomical interferometers in the optical range. What
is measured is the average value of parameters across a spectral band. Knowledge
of the dependence of these parameters with wavelength would be precious and would
bring rich informations on the physical conditions of the sources. A
fundamental limitation to achieve this goal is the atmospheric phenomenon of
optical path fluctuations or piston effect. It has been shown that the method
presented in this paper allows to recover the visibility function with a low
spectral resolution. Visibility moduli are reconstructed with a precision that can
be as good as a few percent between 2 and 2.5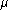 m for S/N ratios greater
than 50. Visibility phase gradients are also very well extracted from the simulated
data with errors that are less than 0.01rad.
m for S/N ratios greater
than 50. Visibility phase gradients are also very well extracted from the simulated
data with errors that are less than 0.01rad.
This reduction algorithm for correction of piston fails to recover the true phase of visibilities.
This is not prejudicial to the spectral analysis of visibilities. A complement to
this algorithm is needed if one wants to remove atmospheric phase errors from
interferometric data to achieve high resolution imaging and will be
presented in a forthcoming paper.
Copyright by the European Southern Observatory (ESO)
web@ed-phys.fr